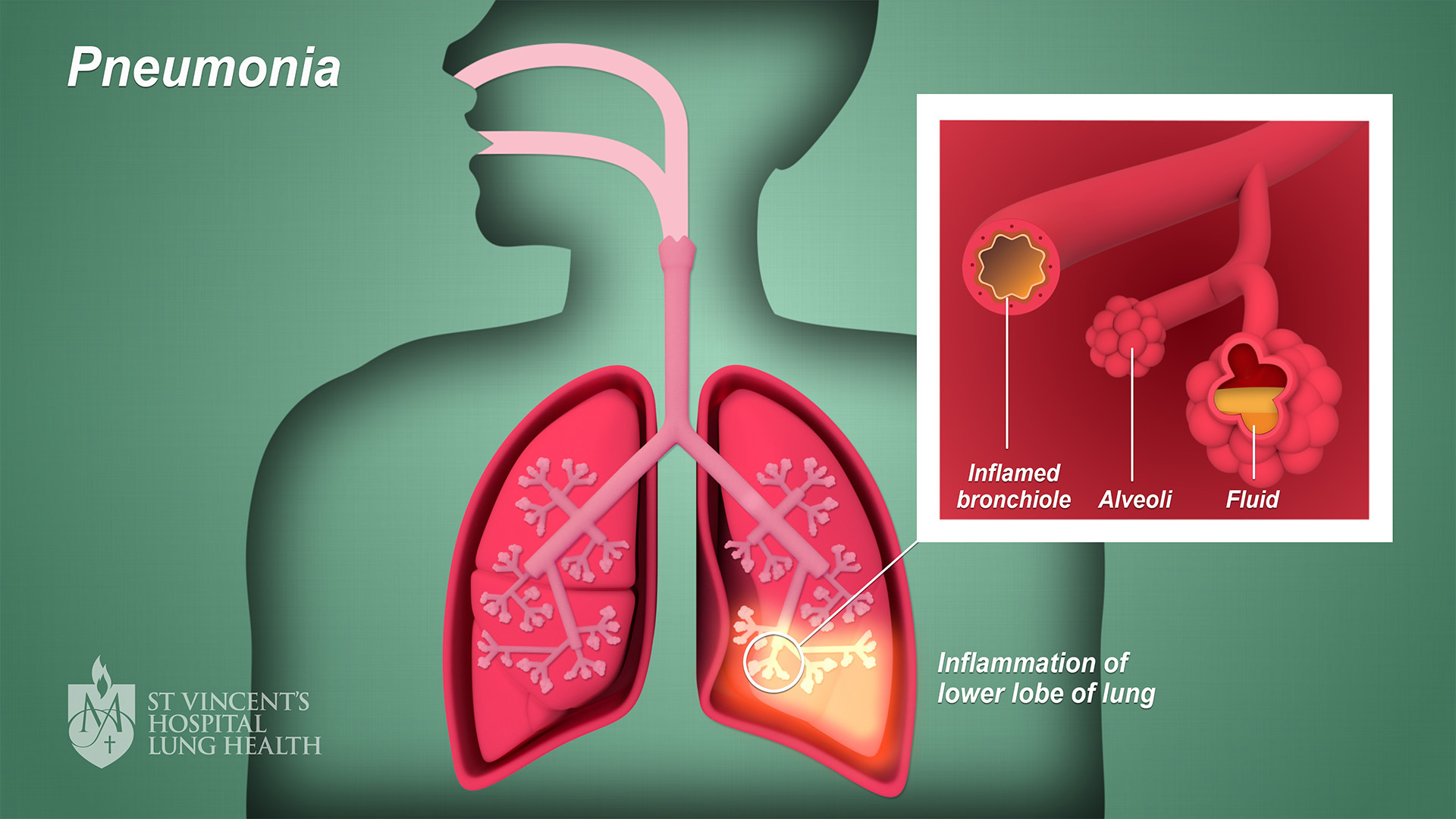
Introduction
Pneumonia results from an infection which causes the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs to become filled with fluid or pus. Pneumonia can develop in either one or both of your lungs. Anyone can develop pneumonia, although those who are under 2 years or over 65 are more at risk due to a lowered immunity (ability to fight infection). As well as asking about your symptoms, there are a number of tests your doctor will undertake to determine, including X-ray scan of your lungs. If the X-ray shows fluid around your lungs, she may do a procedure called a pleural fluid culture, where a sample of fluid is taken to test for infection.
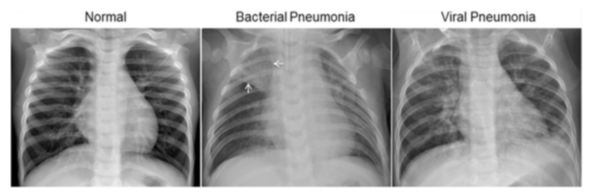
The normal chest X-ray (left panel) depicts clear lungs without any areas of abnormal opacification in the image. Bacterial pneumonia (middle) typically exhibits a focal lobar consolidation, in this case in the right upper lobe (white arrows), whereas viral pneumonia (right) manifests with a more diffuse ‘‘interstitial’’ pattern in both lungs.
http://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(18)30154-5
Objectives
The main objective of this work is to predict if a patient is at risk of having pneumonia or not, based on the chest X-ray image of the patients. To that end, 5,863 X-Ray images of retrospective cohorts of pediatric patients of one to five years old from Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center are used to train and test a Convolutional Neural Network to classify between normal and pneumonia cases.
Description of the dataset
The dataset is organized into 3 folders (train, test, val) and contains subfolders for each image category (Pneumonia/Normal). There are 5,863 X-Ray images (JPEG) and 2 categories (Pneumonia/Normal).
Chest X-ray images (anterior-posterior) were selected from retrospective cohorts of pediatric patients of one to five years old from Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou. All chest X-ray imaging was performed as part of patients’ routine clinical care.
For the analysis of chest x-ray images, all chest radiographs were initially screened for quality control by removing all low quality or unreadable scans. The diagnoses for the images were then graded by two expert physicians before being cleared for training the AI system. In order to account for any grading errors, the evaluation set was also checked by a third expert.
Findings
The developed model could predict if a patient has pneumonia or not with an accuracy score of 91.67 and recall score of 95.64.
Acknowledgements
Data: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/rscbjbr9sj/2
https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia
Link to the code